Mediterranean seasons
Lively Data : November 19, 2007
On several occasions, Lively Data or our other items on the Aviso website, have echoed the ocean seasons : the alternation of the seasons is the main cause of changes in sea level during a year.
It's a simple phenomenon : surface temperature increases as a result of solar radiation, the heat propagates in-depth and while it warms up, there's a water's dilatation. Conversely, if the surface temperature drops, there's water's contraction. This is called steric effect.
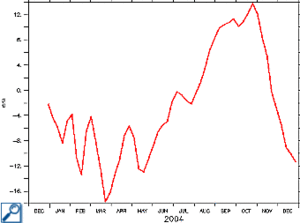
We can observe a difference of about 20 cm to 30 cm in the sea level between the seasons in the Mediterranean Sea, where this phenomenon is amplified by the characteristics of this semi-enclosed sea. This amplitude in sea level anomalies can be revealed on a time serie (year 2004, on the left) at a point of Western Mediterranean (6°E, 40°N) : minimum end of March (-16 cm) and maxima end of October (+14 cm).
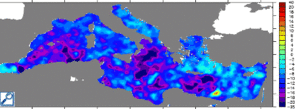
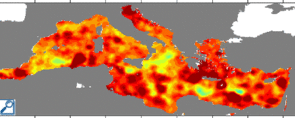
Using the LAS, this seasonal amplitude can also be revealed by representating and comparing the minimum (for the period between mid-March and mid-May) and maximum (for the period between mid-September and mid-November ) of sea level anomalies of each grid point (maps below).
Minima and Maxima of the Sea Level Anomalies computed from merged altimetry data : choose DT - Delayed time Data, DT - Mediterranean, (Maps of) Sea Level Anomalies, then Minimum (or Maximum) in Define variable, Select analysis type. Choose the time "T" in Apply to these Axes, then choose the period. To compare the two periods, it is necessary to saturate the palette colors (parameter Color fill levels in Select Options : (-35)(-20,20,2)(40)).
See also :
- Applications: Mediterranean Sea
- Lively Data, September 22, 2006, Atlantic Ocean with steric effects
![]() Use the Live Access Server
Use the Live Access Server