LRA: Laser Retroreflector Array
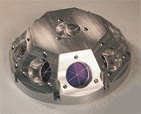
The LRA is an array of mirrors that provide a target for laser tracking measurements from the ground. By analyzing the round-trip time of the laser beam, we can locate very precisely where the satellite is on its orbit.
Function
The LRA is used to calibrate the other location systems on the satellite (Doris, TRSR) with a very high degree of precision.
Principle
| The LRA is a passive instrument that acts as a reference target for laser tracking measurements performed by ground stations. Laser tracking data are analyzed to calculate the satellite's altitude to within a few millimeters. However, the small number of ground stations and the sensitivity of laser beams to weather conditions make it impossible to track the satellite continuously. That is why other onboard location systems are needed. | 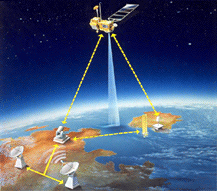 |
Technical data
The retroreflectors are placed on the nadir face of the satellite. The totally passive unit consists of nine quartz corner cubes arrayed as a truncated cone, with one cube in the center and the others arranged azimuthally around the cone. This arrangement will allow laser ranging at field-of-view angles of 360 degrees in azimuth and 60 degrees elevation around the perpendicular. The retroreflectors are optimized for a wavelength of 532 nanometers (green), offering a field of view of about 100 degrees. Jason-1's LRA was built by ITE Inc. under contract to Nasa's Goddard Space Flight Center.