Doris on Jason-2

The Doris instrument onboard Jason-2 will provide real-time location and precise orbit determination. Doris measurements are also used for geophysical studies, in particular through the International Doris Service (IDS). Doris is a dual-frequency instrument able to determine atmospheric electron content.
The main changes from the previous Doris instruments are:
- the instrument will be fully redunded,
- software can be fully reloaded without any mission interruption,
- platform attitude is provided in real time to Doris and used by Diode (on-board Doris navigator); also downloaded by Doris in the science telemetry flow,
- a dosimeter is included in the electronic box, to measure the total radiation dose received by Doris,
- the altimeter will received information from Doris onboard for real-time tracking
Function
Real-time location: Diode
The Diode onboard navigator locates the satellite on orbit in real time. This information is essential for providing altimetry data in real time or near-real time. In 2012, a new Doris/Diode version is proposed for upload on-board Jason-2: the real-time orbit accuracy on the rms of the radial component (for the OGDR) would drop from 3.3 cm down to 2.7 cm (see the poster presented at the OSTST 2011 by C.Jayles et al.: Doris/Diode: recent improvements, pdf).
Precise orbit determination
Doris measurements are used for precise orbit determination (POD).
Ionospheric electron content
By measuring and comparing the path delay of signals transmitted at two separate frequencies, Doris is able to calculate the electron content in the atmosphere. This information is then used to determine perturbations on the altimeter's radar signal.
This function complements the dual-frequency altimeter function.
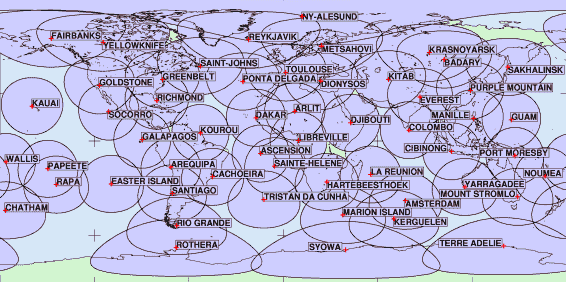
Doris network of orbitography beacons and their spatial coverage
New on Jason-2
Doris Diode real-time location is coupled with Poseidon-3 altimeter, thus enabling better altimeter data acquisition in areas like coastal zones, inland waters and ice. The Doris instrument onboard Jason-2 has several improvements with respect to Jason-1. Among them, it has the capability of receiving and processing onboard as many as seven beacons at the same time (vs. two for Jason-1). This leads to a much higher number of data processed, and should lead to an even better orbit determination.
Principle
Doris orbitography beacons transmit signals at two separate frequencies (2036.25 MHz and 401.25 MHz) to the satellite. The receiver onboard the satellite analyzes the received signal frequencies to calculate its velocity relative to Earth. This velocity is fed into orbit determination models to derive the satellite's position on orbit to within two centimeters on the radial component.

Further information :
- Doris on Aviso website.
- Coupling Doris/Diode with the Poseidon-3 altimeter:
a team effort in orbit . C. Jayles and al. (pdf). - International Doris Service (IDS).




