The Sun and the Moon have a date with the sea
Tides account for some of the most significant variations in sea level. The combined attraction of the Moon and the Sun is behind this phenomenon and its variations.
| The Moon, like the Sun, attracts the Earth and its oceans, which then change their shape. Water accumulates at the place of maximum attraction, in other words at that point on the globe which is the closest to the celestial body. In addition, due to the speed of the movement, an opposing centrifugal force keeps the Earth on its orbit. This centrifugal force pushes the water back and it then accumulates in the opposite direction to the celestial body. If the celestial body (Moon or Sun) is in the Earth's equatorial plane, then there are two high and two low tides per day. | 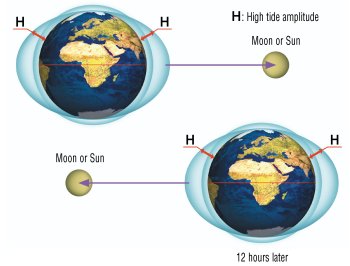 |
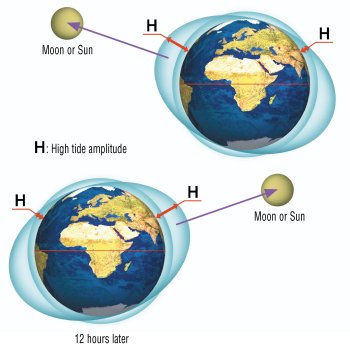 | If the celestial body is not in the equatorial plane, given that there are two high and two low tides per day, then one of the high or the low tides will be greater than the other high or low tide respectively, every day, at middle latitudes. |
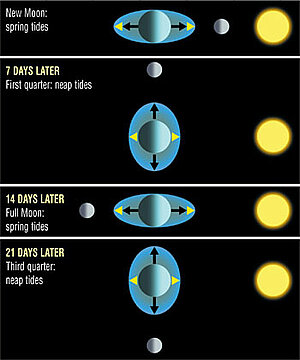
The respective positions of the Moon and Sun in relation to the Earth cause the cycle of monthly variations. When aligned, their influences are reinforced, when at a right angle, they are reduced, which means that tides are or more less high.
In order to be able to calculate tides, it is thus necessary to know the attractive force of the Moon and Sun and their respective positions. The relief of the bottom of the seas and the shape of the coastline also affect tides and can amplify the phenomenon up to fifteen metres, as is the case for the bays of Mont St Michel (France) or Fundy (Canada).
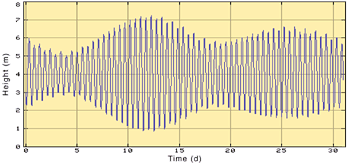 (Credits Shom). |