Sea ice observed by Swot
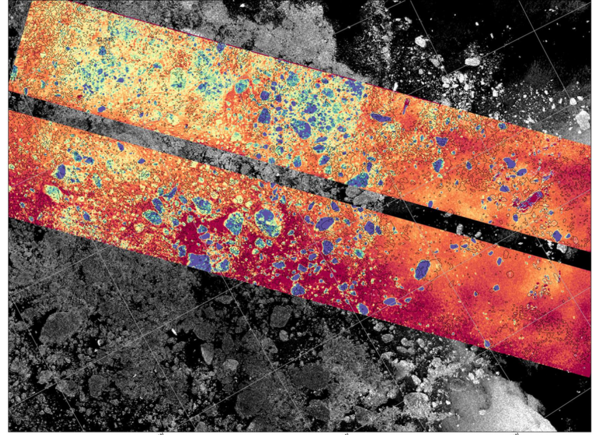
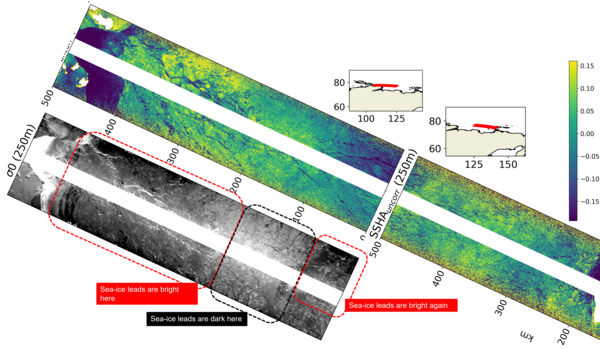
Swot also measures over the frozen areas of the oceans, as its orbit extends to 77.6° North and South. Sea ice has an impact on ocean dynamics, which observation is one of the main objectives of the Swot mission, but these dynamics exist just as much under the ice. In addition, leads, i.e. channels of open waters, are present and vary between sea ice chunks. Their sea surface heights can also be measured in the same way as other sea surface. This enables to estimate the thickness of the sea ice, based on its freeboard, i.e. its height above the waterline.
What's more, the image above shows small pieces of sea ice (or possibly icebergs), carried by currents over the days.
Cristal/Sentinel-9, a European Copernicus satellite mission dedicated to ice, is scheduled for launch in 2027. This satellite will carry an altimeter of the same type as Cryosat-2.