The Silent World disturbed by icebergs' noise
Image of the Month - September 2016
The ocean's nickname of the "Silent world" is largely overdone. From whales' songs to fishes nibbling the corals, sound is very much part of the ocean, even without the humans' sonars and engines. However, a natural sound may not be thought of - the sounds of icebergs.
To be sure, human beings have a role in its increase, but there were icebergs before climate change, and they broke and collided noisily, as they are doing now, only more often.
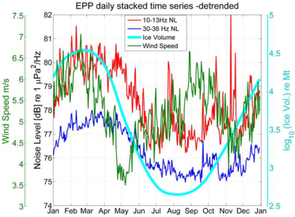
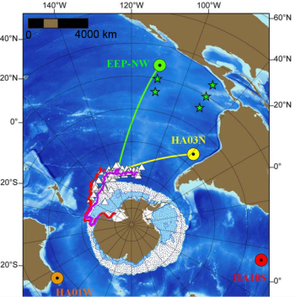
Altimetry do not able to measure sound in the ocean - no more than any other space technique, since the sound does not propagate out of the atmosphere. However, it ables to estimate iceberg concentration. Comparing in situ acoustic measurements and altimetry-based iceberg concentration show some correlations at given frequencies with specific events like the calving of B15A and C19 icebergs from the Ross ice shelf in Antarctica. The noise of such events could reach (with a time lag) up to the Equatorial area, and is dominating the Southern hemisphere oceans. And any increase in iceberg calving will thus have an impact on the Southern oceans soundscape.
See also:
- Image of the Month, September 2013: Icebergs on the move
- Image of the Month, November 2008: Counting icebergs
- Applications: Ice sheets and sea ice
- Data: Waveforms
Other website on this subject:
- the database used to produce those plots are available throught Ifremer's Cersat center, at ftp://ftp.ifremer.fr/ifremer/cersat/products/gridded/altiberg/
References:
- Matsumoto, H., D.W. R. Bohnenstiehl, J. Tournadre, R. P. Dziak, J. H. Haxel, T.-K. A. Lau, M. Fowler, and S. A. Salo (2014), Antarctic icebergs: A significant natural ocean sound source in the Southern Hemisphere, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 15, 3448–3458, doi:10.1002/2014GC005454.